3-Axis vs 4-Axis vs 5-Axis CNC Milling: Which One Should You Choose?
In modern precision machining, CNC milling machines are the backbone of innovation. These versatile machines can create highly complex components with exceptional accuracy and repeatability. But here’s the catch—not all CNC mills are the same. One of the most critical differences between them lies in the number of axes they operate on. That alone can determine the type of parts you can produce, your production speed, and your overall efficiency.
Choosing between 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC milling machines is no easy task, especially when each brings unique advantages. To help you make the right decision, we’ll dive into what each machine type offers, compare their differences, and highlight the best applications for each. Whether you’re an engineer, manufacturer, or business owner, this guide will help you select the CNC milling machine that aligns with your production needs.
Quick Comparison: 3-Axis vs 4-Axis vs 5-Axis CNC Milling
Before going into details, let’s briefly outline the fundamental differences:
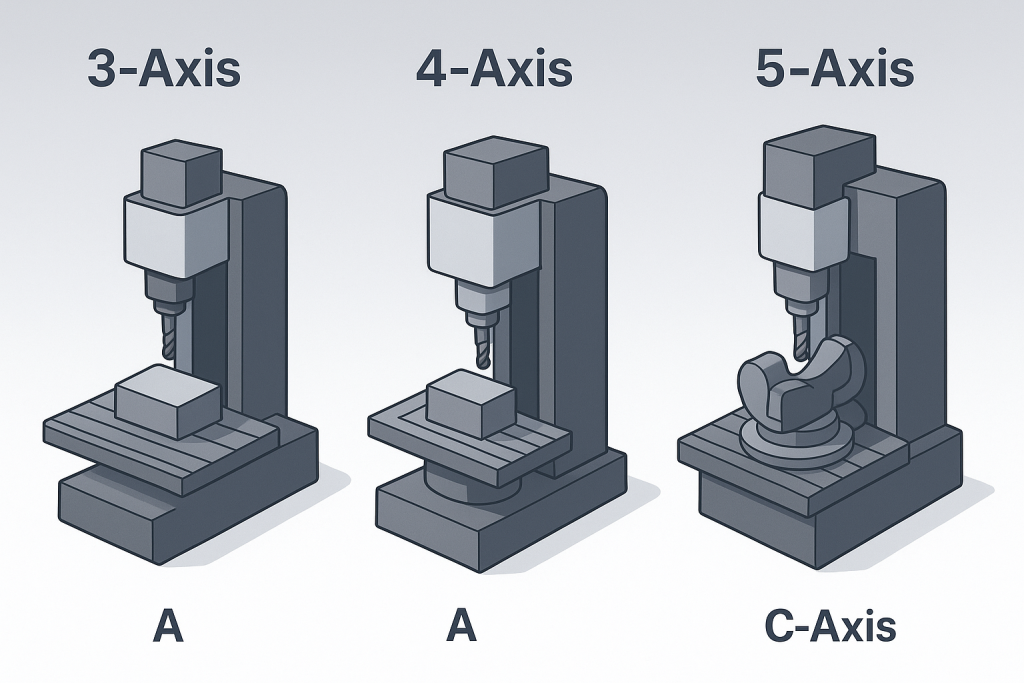
- 3-axis machines: Movement along the X, Y, and Z axes. Great for basic machining tasks, 2D and 2.5D parts, and cost-effective projects.
- 4-axis machines: Add a rotational axis (usually around X, known as the A-axis). Allows machining on multiple sides in one setup.
- 5-axis machines: Movement along three linear axes plus two rotational axes (A/B and C). Capable of handling the most complex parts in a single setup with unmatched precision.
3-Axis CNC Milling
How It Works
A 3-axis CNC milling machine operates using a Cartesian coordinate system:
- X-axis: Horizontal movement (left to right)
- Y-axis: Horizontal movement perpendicular to X (front to back)
- Z-axis: Vertical movement (up and down)
By controlling these three axes, the CNC machine can move the cutting tool along programmed paths to shape the workpiece. The process supports operations such as:
- Facing (flattening surfaces)
- Drilling (creating holes)
- Boring (enlarging holes with precision)
- Pocket milling (cutting cavities)
- Contouring (machining edges and profiles)
Capabilities
- Suitable for 2D and 2.5D machining
- High precision and smooth finishing
- Versatile across many materials (plastic, aluminum, steel, titanium)
- Cost-effective compared to advanced CNC machines
Limitations
- Limited in machining complex geometries
- Requires multiple setups for parts with features on different sides
- Struggles with undercuts and hidden geometries
- Increased setup time for complex parts
Best Applications
- Prototyping (cost-effective, fast turnaround)
- Flat or simple parts
- Small to medium production runs
- Training and education for CNC basics
Industries That Rely on 3-Axis Milling
- Automotive: engine brackets, brake components
- Aerospace: structural panels, housings
- Electronics: casings, heat sinks
- General manufacturing: wide range of industrial parts
4-Axis CNC Milling
How It Works
A 4-axis CNC milling machine builds on 3-axis capability by adding a rotational axis—most commonly the A-axis, which rotates around the X-axis. This allows the machine to cut on multiple sides of a part without manual repositioning.
There are two main implementations:
- Rotary table: Workpiece mounted on a rotating platform
- Indexing head: Workpiece held in a rotating spindle
With this configuration, machining operations can be performed on the circumference of cylindrical parts, helical features, and multiple faces of a workpiece.
Capabilities & Advantages
- Multi-sided machining in one setup → reduced handling time
- Improved surface finish on curved surfaces
- Creation of helical features (threads, spiral grooves)
- Higher efficiency than 3-axis due to fewer repositioning steps
- Greater accuracy by eliminating cumulative errors from multiple setups
Limitations
- Still limited in creating complex undercuts
- Many machines operate in 3+1 mode, not true simultaneous 4-axis
- More expensive than 3-axis in both investment and maintenance
- Requires more advanced programming skills
Best Applications
- Cylindrical parts (pipes, shafts, spindles)
- Multi-sided parts needing machining in fewer setups
- Helical geometries (threads, grooves)
- Complex profiles requiring rotational cutting
Industries That Benefit from 4-Axis Milling
- Medical devices: implants, surgical tools
- Aerospace: turbine blades, contoured structures
- Automotive: transmission housings, engine parts
- Mold-making: molds with complex parting lines
5-Axis CNC Milling
How It Works
A 5-axis CNC milling machine is the most advanced configuration. It combines three linear axes (X, Y, Z) with two rotational axes (A/B and C). This enables the cutting tool or workpiece to be positioned at almost any angle.
- X, Y, Z → linear movement
- A/B-axis → rotation around X or Y
- C-axis → rotation around Z
This freedom of movement allows machining of extremely complex parts in one setup.
Types of 5-Axis Machines
- 3+2 axis (positional 5-axis): Uses the two rotational axes to orient the part, then locks them while machining in 3 axes.
- Simultaneous 5-axis: All five axes move simultaneously, enabling the most complex and contoured surfaces.
Capabilities & Advantages
- Ability to machine complex geometries (impellers, turbine blades)
- Single-setup machining for highly intricate parts
- Superior surface finishes due to optimal tool orientation
- Extended tool life through reduced tool stress
- Reduced cycle times for multi-sided machining
- Ability to machine deep pockets and undercuts
- Best possible part accuracy
Limitations
- High investment cost
- Complex programming with steep learning curve
- Greater maintenance requirements
- Overkill for simple parts
Best Applications
- Aerospace components: turbine blades, impellers, structural supports
- Medical devices: orthopedic implants, dental prosthetics
- Mold-making: intricate molds with fine detail
- Automotive: cylinder heads, high-performance parts
- Energy sector: turbines, pump impellers
- Artistic/architectural: sculptures, decorative elements
Industries That Leverage 5-Axis Milling
- Aerospace and defense
- Medical and dental
- Automotive performance engineering
- Energy and power generation
- Luxury goods & design
Comparison Table: 3-Axis vs 4-Axis vs 5-Axis CNC Milling
| Feature | 3-Axis | 4-Axis | 5-Axis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Axes of movement | X, Y, Z | X, Y, Z, A | X, Y, Z, A/B, C |
| Complexity of parts | Low–Medium | Medium–High | High–Very High |
| Setup time for complex parts | Long | Medium | Short |
| Machining of undercuts | Limited | Improved | Excellent |
| Multi-sided machining | Manual repositioning required | Possible in one setup | Single setup for most parts |
| Programming complexity | Low | Medium | High |
| Machine cost | Low | Medium | High |
| Ideal for small batch production | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Ideal for large-scale production | Yes | Yes | Yes, with highest efficiency |
| Learning curve | Low | Medium | High |
| Common industries | General manufacturing, automotive | Medical, aerospace, custom machining | Aerospace, medical, mold-making |
Work With KingsMG to Start Your CNC Milling Projects
At KingsMG, we bring the world of CNC machining to your fingertips. With cutting-edge machines ranging from Fanuc 3-axis CNC, Makino 4-axis CNC, to Hermle 5-axis CNC milling centers, we can meet every production requirement with precision and speed.
Whether you’re looking to prototype a simple part, mass-produce automotive components, or manufacture intricate aerospace structures, our expert team will tailor solutions to your needs. KingsMG combines technology, experience, and innovation to ensure your CNC milling projects meet the highest standards of accuracy and efficiency.
From intricate custom designs to large-scale industrial runs, KingsMG is your trusted partner in modern CNC machining.
Conclusion
The decision between 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC milling depends entirely on your project needs:
- Choose 3-axis if you want a cost-effective solution for 2D and moderately complex parts.
- Go with 4-axis if you need multi-sided machining with better efficiency at a reasonable cost.
- Invest in 5-axis if your focus is on highly complex parts, aerospace-grade components, or precision-critical industries.
By understanding the capabilities, limitations, and ideal applications of each machine, you can optimize your production efficiency, part quality, and overall costs.
And when you’re ready to unlock the full potential of CNC milling, KingsMG is here to turn your vision into reality. Contact us today to start your CNC machining journey!